Answer:
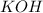
Step-by-step explanation:
Here, we want to get the limiting reactant
The limiting reactant is the reactant that produces less amount of the product
Firstly, let us get the number of moles of the reactants
To get that, we have to divide the mass of the reactant by the molar mass
For Potassium Hydroxide, we have its molar mass as 56 g/mol
Thus, the number of moles of KOH that reacted will be:
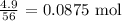
From the equation of reaction:
3 moles KOH produced 1 mole K3PO4
0.0875 KOH will produce:
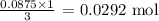
For H2O, 0.0875 mole will be produced as the two have equal coefficients
For H3PO4, its molar mass is 98 g/mol
The number of moles that reacted will be:
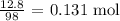
K3PO4 and H3PO4 have the same coefficients. Thus, the number of moles of K3PO4 produced will be 0.131 mol
For H2O, we have:
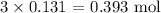
What was produced with KOH was lesser and that makes it the limiting reactant