Given,
The mass of an object is m = 3 kg
Initial temperature, T1 = 400 K
The specific heat of this object is c = 478 J/kg.K
The heat is Q = 13 kJ
Let T2 be the final temperature.
The formula is used to calculate the final temperature.
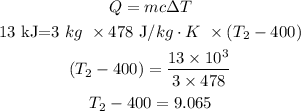
Thus, the value of the final temperature is
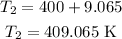
Therefore, the given answer (a) is correct.