The population is increasing by a continuous exponential growth model. Then, it follows the next formula:
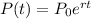
Where P=2265, Po= ?, r=15% = 0.15 and t=5.
P = final population
P0= initial population
r= rate
t= time
Replacing with the given values:
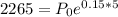
Solve for Po:
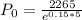
Then
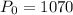
Hence, the number of bacteria in the initial sample is 1070.
(The value is rounded to the nearest integer).