This problem relies on the law of conservation of energy
The equation below is the formula for kinetic energy
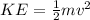
And the formula for gravitational potential energy is
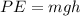
So to find final speed, we will use both of these formulas
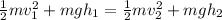
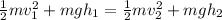
This formula gives us the energy before and after the skier moves up the hill.
For variables, we have
v1 = 16 m/s
mass = 60 Kg
h2 = 2.5 m
h1 = 0 m
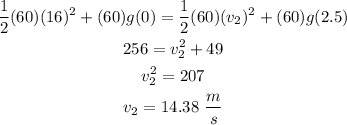
Final Velocity is 14.38 m/s