ANSWER
-10 m/s²
Step-by-step explanation
The displacement of the particle is,

We know that the final velocity is 10m/s, after 2 seconds. To find the acceleration, we have to find the initial velocity too.
We know that the displacement is,
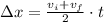
Solving for the initial velocity vi,
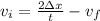
Replace with the values,
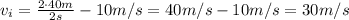
The final velocity is also a function of the acceleration,
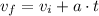
Solving for a,
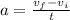
Replace with the values,
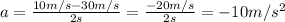
Hence, the acceleration of the particle is -10m/s².