Consider the theorem that when a pair of transversals intersect more than two parallel lines, then the ratio of the corresponding segments are always equal.
According to the given problem,
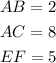
In the given figure, lines ABC and DEF intersect the set of parallel lines 'l', 'm', and 'n'.
Applying the above theorem,
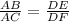
The expression can be resolved as,
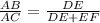
Substitute the values,
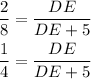
Transpose the terms to simplify,
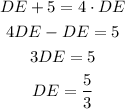
Thus, the value of the segment DE is 5/3 units.