Answer:
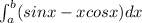
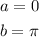
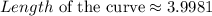
Step-by-step explanation:
Given the function;
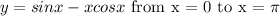
So to find the area of the curve defined by the above, we have to compute;
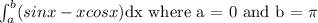
Let's go ahead and determine the length of the curve as seen below;
![\begin{gathered} \int_0^(\pi)(sinx-xcosx)dx \\ =\int_0^(\pi)sinxdx-\int_0^(\pi)xcosxdx=[-cosx]_0^(\pi)-[xsinx+cosx]_0^(\pi) \\ =[-cos(\pi)-(-cos(0))]-[(\pi sin\pi+cos\pi)-(0sin0+cos0)] \\ =[-(-1)-(-1)]-[(\pi(0)+(-1))-[0+(1)] \\ =2-(-2) \\ =2+2 \\ =4 \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/w4pq52gtsnt8kk2l2io1o78dj8k82ad3qh.png)
Given the below midpoint Riemann sum formula;
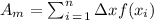
where;

Let's determine the width of each rectangle as seen below;
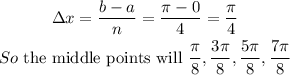
We can now go ahead and solve for A as seen below;
![\begin{gathered} A_m=\Delta x[f((\pi)/(8))+f((3\pi)/(8))+f((5\pi)/(8))+f((7\pi)/(8))] \\ A_m=(\pi)/(4)(0.0199+0.4730+1.6753+2.9223) \\ A_m=0.7854(5.0905) \\ A_m=3.9981 \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/nigiosxyj9leek49jbsev394ruq6xwjkw3.png)
So an approximate value of the length of the curve using the middle Riemann sum is 3.9981