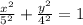Given:
Vertices:
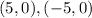
Co-vertices:
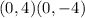
To find: The ellipse equation
Step-by-step explanation:
The general form of ellipse equation is,
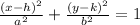
Where (h, k) is the center and a and b are the length of the semi-major and semi-minor axis.
Here,
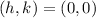
The length of the major axis is the distance between the vertices.
![\begin{gathered} d=\sqrt[]{(x_2-x_1)^2+(y_2-y_1)^2} \\ =\sqrt[]{(0-0)^2+(-5_{}-5)^2} \\ =\sqrt[]{10^2} \\ =10\text{ units} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/j3rgeqkidpsfxap4m11l15eutu6vt6nchh.png)
The length of the minor axis is the distance between the co-vertices.
![\begin{gathered} d=\sqrt[]{(x_2-x_1)^2+(y_2-y_1)^2} \\ =\sqrt[]{(-4-4)^2+(0-0)^2} \\ =\sqrt[]{8^2} \\ =8\text{ units} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/wzzlxarmoll1ycbvr0cv7skssldg9l5fmg.png)
Therefore,
The length of the semi-major axis is 5
The length of the semi-minor axis is 4
So, the standard form of an ellipse equation becomes,
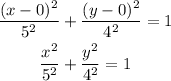
Final answer:
The standard form of an ellipse equation becomes,