We can solve this by using the equations of kinematics below
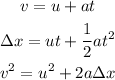
(a).
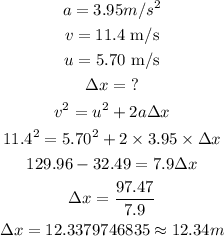
(b)
Since the object moves in a straight part the distance will also be 12.34 m.
(c)
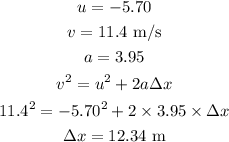
(d)
The total distance is just the total distance covered without direction. In part c the initial velocity was negative, this means it traveled in the opposite direction therefore that part distance can be calculated below
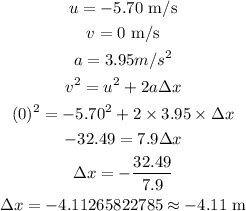
Then the path where the initial velocity was zero and the final velocity was 11.4 m/s can be calculated as follows
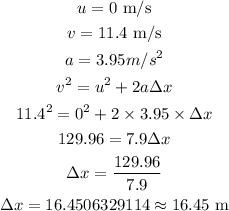
Therefore,
total distance = 4.11 m + 16.45 m = 20.56 m