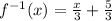
1) To find the inverse function of a linear one, we must follow some steps:
2) Take the given function, and swap the variables so
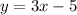
It's going to become in the process:
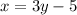
3) And rewrite it putting y on the left side:
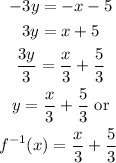
So that's our inverse function whose Range is the Domain of the original one and the Domain is the Range of the original one.