Step-by-step explanation:
We are given: bond energy of C-O = 358kJ/mol
: bond energy of O2 = 498kJ/mol
: bond energy of CO2 = 799kK/mol
Bond energy of reactants:
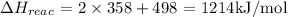
Bond energy of products:
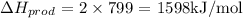
Total change in bond energy:
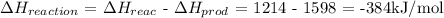
Answer:
Enthalpy of formation = -384kJ/mol