Newton's law of cooling relates the temperature of an object with the time. This law is the following:
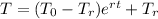
Where:

Since we are asked to determien time we need to solve for "t". To do that we will subtract the temperature of the surrounding from both sides:
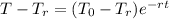
Now, we divide by the factor multiplying "e":
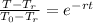
Now, we use natural logarithm on both sides:
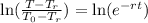
Now, we use the following property of logarithms on the right side:
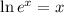
This means that we can lower the exponent, like this:
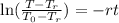
Now, we divide both sides by "-r":
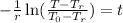
Now, we substitute the values:
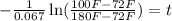
Solving the operations:
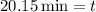
Therefore, the time to wait is 20.15 minutes.