zero
Step-by-step explanationwe know that when derivantind the position function respecto to time we got the function for velocity, so we can integrate the given function to obtain the function for velocity
hence
Step 1
a) integrate to find the function for distance travelede
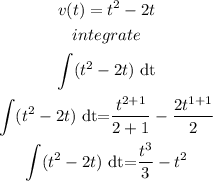
so
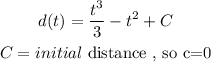
Step 2
now,we have the functio for the distance,
a) evaluate for t=0
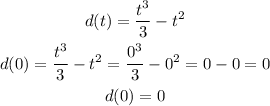
b) evaluate for t=3 minutes
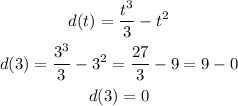
now, find the total distance traveled by the particle from t = 0 to t = 3 minutes., subtract the positions
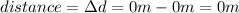
so, the total displacement would be zero,but :
the particle actually travels ,it start in negative direction,and then it moves to positive direction, after 3 minutes the particle is in the same place
so, the answer is zero