Answer:
The answer is below
Step-by-step explanation:
Given that:
Hot reservoir temperature (
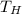 ) = 550 K, Cold reservoir temperature (
) = 550 K, Cold reservoir temperature (
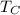 ) = 300 K, power input (
) = 300 K, power input (
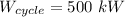 ), cycle's coefficient of performance(
), cycle's coefficient of performance(
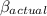 ) = 1.6
) = 1.6
a) The rate of energy removal in the cold reservoir (
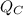 ) is given by the formula:
) is given by the formula:
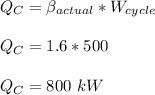
b) The maximum cycle's coefficient of performance(
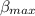 ) is:
) is:
