To begin, we first find the measure of the internal angles of the regular hexagon, using the formula below:
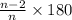
Since a hexagon is six-sided, we have that n = 6. So:
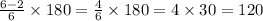
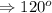
Thus, we have each internal angle to be 120 degrees.
Now, we consider the triangle ABC formed in the figure shown in the question.
- We know that
- Also, we know that all the sides of a regular ploygon are always equal and so AB = BC = 4 in.
Thus, we can redraw the figure, as shown below:
Now, we simply apply the Cosine rule to triangle ABC in order to obtain x, which is the length of side AC.
By cosine rule, we have:
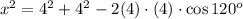
Simplifying gives:
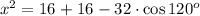
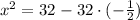
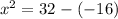
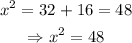
![\begin{gathered} \Rightarrow x=\sqrt[\square]{48} \\ \Rightarrow x=\sqrt[]{16*3}=\sqrt[\square]{16}*\sqrt[\square]{3}=4*\sqrt[\square]{3} \\ \Rightarrow x=4\sqrt[]{3}\text{ in.} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/t7g6yher36jqcb2ogens53j5q6zutvp7xe.png)
Therefore, the length of the diagonal AC is:
![4\sqrt[]{3}\text{ in.}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/wyhk1vc0wwewyteqp2o7yyoii475uvyjfr.png)
Correct answer: option A