Answer:
a) The temperature on the outer surface of the pipe is approximately 179.97 °C
b) The thickness of the insulation is approximately 0.857 m
Step-by-step explanation:
We have;
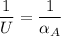
αA = 200 W/(m²·K)
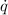 = (T₂ - T₁) × U
= (T₂ - T₁) × U
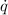 = (200 - 180) × 200 = 4,000
= (200 - 180) × 200 = 4,000
For the pipe, we have;
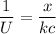
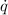 /U= (T₂ - T₁)
/U= (T₂ - T₁)
∴ 4000×
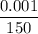 = (180 - T₂)
= (180 - T₂)
T₂ ≈ 179.97 °C
The temperature on the outer surface of the pipe, T₂ ≈ 179.97 °C
b) For the insulation, we have;
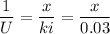
T₂ - T₃ = 179.97 °C - 40°C ≈ 139.97°C
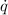 /U= (T₂ - T₃)
/U= (T₂ - T₃)
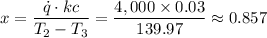
The thickness of the insulation, x ≈ 0.857 m