we have the expression
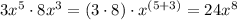
the Pythagorean theorem, states that, in any right triangle
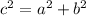
where
c is the hypotenuse of the right triangle
a and b are the legs of the triangle (a and b are perpendicular sides)
Problem N1
hypotenuse ------> c
the opposite side to given angle -----> a
the adjacent side to given angle -----> b
Problem N 2
hypotenuse -----> d
the opposite side to given angle ----> f
the adjacent side to given angle ----> e
In this picture, we have a right triangle
the hypotenuse is always the greater side -------> c
the legs a and b are always the perpendicular sides
If the reference angle is alpha
then
the adjacent side is a and the opposite side is b
If the reference angle is beta
then
the adjacent side is b and the opposite side is a
in both cases, the hypotenuse is always the same (c)