In order to calculate the projection of u on v, we can use the formula below:
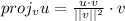
First, let's define the vectors u and v from the image:
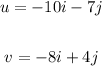
Now, let's calculate the dot product on the numerator:
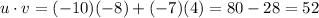
The denominator can be calculated as the dot product of v and itself:
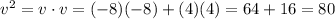
Therefore the projection is given by:
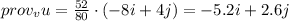
Correct option: the second one.