Step-by-step explanation
In this problem, we have a graph of the PDF (Probability Density Function). To compute probabilities in a certain interval (a, b), we must integrate this function from x = a to x = b.
(1) P(X ≤ 22)
We integrate the function from x = -∞ to x = 22, we get:
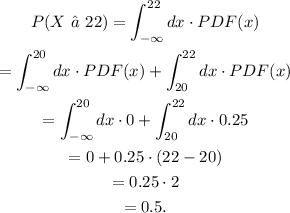
We separated the integral to use the data from the graph.
(2) P(X > 21)
We integrate the function from x = 21 to x = ∞, we get:
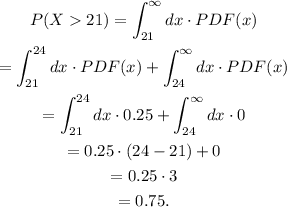
(3) The Q1 is the value x = a of the interval (-∞, a) that gives a probability equal to 0.25. So we must find x such that:
![P(XUsing the data of the graph, we have:[tex]\begin{gathered} \int_(-\infty)^adx\cdot PDF(x)+\int_(20)^adx\cdot PDF(x)=0.25, \\ \int_(-\infty)^(20)dx\cdot0+\int_(20)^adx\cdot0.25=0.25, \\ 0.25\cdot(a-20)=0.25, \\ a-20=(0.25)/(0.25), \\ a-20=1, \\ a=21. \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/high-school/f66xy2m27f5orn2eckrevjj0qj2s7yrv2q.png)
(4) The median is the value x = a of the interval (-∞, a) that gives a probability equal to 0.5. Proceeding as before, we have:

(5) The Q3 is the value x = a of the interval (-∞, a) that gives a probability equal to 0.75. Proceeding as before, we have:
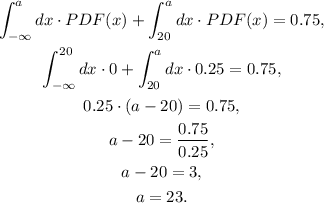
(6) The IQR is given by the difference between Q3 and Q1. Using the results from above, we get:
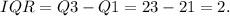
Answer
• P(X ≤ 22) = 0.5
,
• P(X > 21) = 0.75
,
• Q1 = 21
,
• median = 22
,
• Q3 = 23
,
• IQR = 2