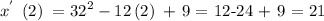Answer:
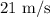
Step-by-step explanation:
Here, we want to get the velocity of the particle when the acceleration is zero
From the question, we have to differentiate twice to get the acceleration:
Now, let us get the value of t wt which acceleration is zero:
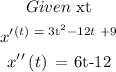
Now, let us calculate the t value when the second differential is zero
Mathematically, we have that as:
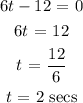
What this simply means is that the acceleration is zero when t = 2
Now, let us get the velocity when t = 2
We simply substitute the value of t into the first differential
Mathematically, we have that as: