The Reaction :
2NH3 (g) + CO2 (g) → CO(NH2)2 + H2O
NH3 Ammonia
CO2 Carbon dioxide gas
CO(NH2)2 Urea
H2O water
Don't forget to balance your equation.
a) To get the volume of NH3 we need to assume Ideal gas conditions.
Ideal Gas Law:
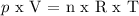
Step 1) We calculate the moles of NH3 that we need to obtain 600 g of Urea, so:
The molar mass of Urea = 60 g/mol (approx.)
From the reaction, we know that:
2 x 1 mole of NH3 ---------- 60 g of Urea
X ---------- 600 g of Urea
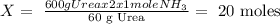
n (moles) NH3 = 20 moles
Step 2) We clear the volume (V) from Ideal Gas Law:
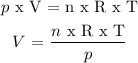
n = moles of NH3 = 20 moles
T = absolute temperature = 37 °C + 273 = 310 K
p = pressure = 105 kPa
R = gas constant = 8.31 kPa x m3 / mol x K
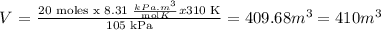
Answer: V (NH3) = 410 m3
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
b) It is the same procedure above.
Moles of CO2:
1 mol of CO2 ------ 60 g of Urea
Y ------- 600 g of Urea
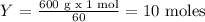
From Ideal gas law:
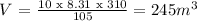
Answer: V(CO2) = 245 m3