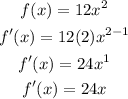We are given the function:
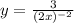
To rewrite this, we need to remember that negative exponents mean the reciprocal of the expression. So we get:
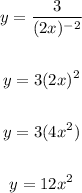
To differentiate, we bring down the exponent as a multiplier, then reduce the original exponent by 1.
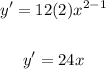
The derivative of f(x) = x^a is f'(x) = ax^(a-1).
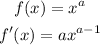
So if we are looking for f'(x) when f(x) = x^2,
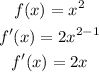
Applying this to our function f(x) = 12x^2, we get: