ANSWER
Oxygen is the limiting reactant in the reaction
Step-by-step explanation
Given information
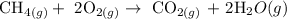
The mole of methane is 1.5 moles
The mole of oxygen is 2.0 moles
To determine the limiting reactant in the reaction above, follow the steps below
Step 1: Write the formula for calculating the limiting reactant in a reaction
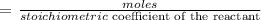
Step 2: write the stoichiometric coefficient of the reactants in the above equation
The stoichiometric coefficient of methane is 1
The stoichiometric coefficient of oxygen is 2
Step 3: Divide the mole of the reactants by their stoichiometric coefficient
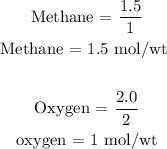
From the above calculations, you will see that oxygen has the least mole per weight.
Therefore, oxygen is the limiting reactant in the above reaction