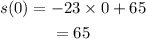The acceleration of the particle is given by the formula mentioned below:
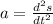
Differentiate the position vector with respect to t.
![\begin{gathered} (ds(t))/(dt)=(d)/(dt)\sqrt[]{\mleft(t^3+1\mright)} \\ =-(1)/(2)(t^3+1)^{-(1)/(2)}*3t^2 \\ =(3)/(2)(t^2)/(√((t^3+1))) \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/ey0aiy8gmtf7mbhq8dbxvkwsn0ejgdwasj.png)
Differentiate both sides of the obtained equation with respect to t.
![\begin{gathered} (d^2s(t))/(dx^2)=(3)/(2)(\frac{2t}{\sqrt[]{(t^3+1)}}+t^2(-(3)/(2))*\frac{1}{(t^3+1)^{(3)/(2)}}) \\ =\frac{3t}{\sqrt[]{(t^3+1)}}-(9)/(4)\frac{t^2}{(t^3+1)^{(3)/(2)}} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/18cb068tuzdz27c3l13bx9nqe6dro10s10.png)
Substitute t=2 in the above equation to obtain the acceleration of the particle at 2 seconds.
![\begin{gathered} a(t=1)=\frac{3}{\sqrt[]{2}}-\frac{9}{4*2^{(3)/(2)}} \\ =1.32ft/sec^2 \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/ywzequt8qkradjr5qnh5mlqh6e6t4ben30.png)
The initial position is obtained at t=0. Substitute t=0 in the given position function.