We can see the following given data table:
And from this table, we have to find the five-number summary.
The five-number summary gives us:
• The minimum value for the data set
,
• The first quartile (Q1): this is a value for which 25% of the observations are below it, and 75% of the observations are above it.
,
• The median (50% of the observations are above (and below) this value.
,
• The third quartile (Q3): this is a value for which 75% of the observations are below it, and 25% of the observations are above it
,
• The maximum value for the data set
Then to find those numbers, we can proceed as follows:
1. We have to rewrite the information from the data as a list, and we have to take into account the frequencies for each observation:
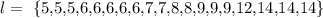
And we already have the observations ordered in ascending order. The total of observations is 19 cases.
2. Now we can find the minimum and the maximum values as follows:
• Minimum value = 5
,
• Maximum value = 14
3. We have to find the median as follows:
Since we have that the total number of observations is 19, and this is an odd number, then the median is the middle value. In this case, below the median, we have 9 values, and above it, 9 values too.
Therefore, the median is equal to 7.
4. Find the first quartile (Q1) and the third quartile (Q3)
The first quartile, roughly speaking, is the median for the first half of the values, and we can say that the third quartile is the median for the second half of the values. Then we have:
We use here the Method of Moore and McCabe in which we do not include the median in finding both values.
Therefore, Q1 = 6, and Q3 = 9.
Therefore, in summary, the five-number summary can be written as follows:
Min = 5
Q1 =