Step-by-step explanation
In this problem, we have the following functions:
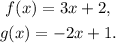
(a) The function (f + g)(x) is given by:
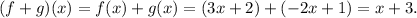
(b) Using the previous result, and replacing x = 6, we get:
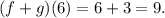
(c) The function (f · g)(x) is given by:
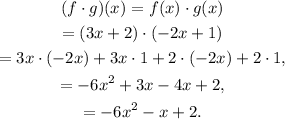
(d) The function (f - g)(x) is given by:
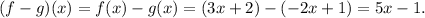
(e) The function (f/g)(x) is given by:
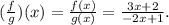
The domain of this function is all the real numbers except the numbers that make zero the denominator because we can't divide by zero. The denominator is 0 when:
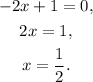
So the domain of the function is:
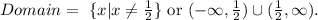
Answer
(a) (f + g)(x) = x + 3
(b) (f + g)(6) = 9
(c) (f · g)(x) = -6x² - x +2
(d) (f - g)(x) = 5x - 1
(e) Domain = x = (-∞, 1/2) U (1/2, ∞)