Solution:
The standard equation of a hyperbola is expressed as
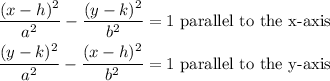
Given that the hyperbola has its foci at (0,-15) and (0, 15), this implies that the hyperbola is parallel to the y-axis.
Thus, the equation will be expressed in the form:
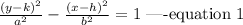
The asymptote of n hyperbola is expressed as
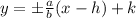
Given that the asymptotes are
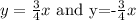
This implies that
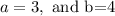
To evaluate the value of h and k,
![undefined]()