Let's call the longer leg "a", the shorter leg "b" and the hypotenuse "c".
So, if "a" is 10 cm shorter than twice the length of "b", we have:
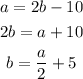
And if "c" is 20 cm longer than "a", than:
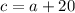
We also know the Pythagorean Theorem to be:
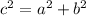
We can substitute "b" and "c" into it to find out "a":
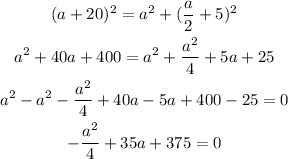
Now we have to use Bhaskara's Formula to find a, so:
![\begin{gathered} a=\frac{-35\pm\sqrt[]{35^2-4\cdot(-(1)/(4))\cdot375}}{2\cdot(-(1)/(4))}=\frac{-35\pm\sqrt[]{1225+375}}{-(1)/(2)}=-2(-35\pm\sqrt[]{1600})=-2(-35\pm40) \\ a_1=-2(5)=-10 \\ a_2=-2(-75)=150 \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/n6lqrp7eb0u6gnypbch9dbsm4ocwwzvje5.png)
Since we can't have a negative lentgh, we have a = 150 cm.
Now we use the equations to find "b" and "c":
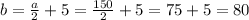
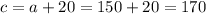
Finally, we have a = 150 cm, b = 80 cm and c = 170 cm.