Consider that the given figure depicts two intersecting lines, thereby forming 4 angles.
These angles can be referred to as the upper angle (U), lower angle (L), left side angle (LS), and right side angle (RS).
According to the given information,
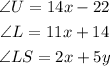
Theorem: The vertically opposite angles formed by the intersection of two lines are always equal.
It follows that,
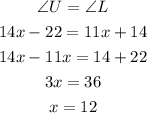
Theorem: The sum of angles constituting a straight line is always 180 degrees.
It follows that,
Now that we know the values of the variables 'x' and 'y', the values of the angles can be obtained as follows,
![undefined]()