We are given the following information
Mass of car = 950 kg
Initial speed of car = 16.0 m/s
Final speed of car = 9.50 m/s
Time = 1.20 s
The average force exerted on the car during braking can be found using Newton's 2nd law of motion
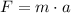
Where m is the mass of the car and a is the acceleration of the car.
The acceleration of the car is given by
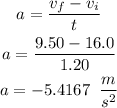
The negative sign indicates deacceleration since the car is stopping.
So, the force is
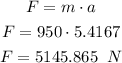
Therefore, an average force of 5145.865 N was exerted on your car during braking.
The distance traveled by the car while braking can be found as
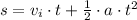
Let us substitute the given values
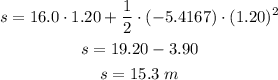
Therefore, the car traveled a distance of 15.3 m while braking.