Answer with explanation: Provided the satellitle orbiting the earth ( Planet ), we have to fill the missing information in the blanks:
Acceleration of the satellite:
![\begin{gathered} a=-g \\ g=(M)/(r^2)G \\ G=6.674\cdot10^(-11)\cdot m^3\cdot kg^(-1)\cdot s^(-2) \\ r=(5.81*10^7)m \\ M=(5.97*10^(24))\operatorname{kg} \\ \therefore\Rightarrow \\ g=\frac{(5.97*10^(24))\operatorname{kg}}{(5.81*10^7m)^2}\cdot(6.674\cdot10^(-11)\cdot m^3\cdot kg^(-1)\cdot s^(-2)) \\ g=-6.8578\cdot10^6ms^(-2) \\ a=-g \\ \therefore\Rightarrow \\ a=-(-6.8578\cdot10^6ms^(-2)_{})= \\ a=6.8578\cdot10^6ms^(-2) \end{gathered}]()
Value of G-Constant:
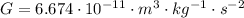
Mass of Earth:
![M=(5.97*10^(24))\operatorname{kg}]()
Radius or distance between the earth and the satellite:
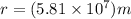
The velocity of the satellite:
![\begin{gathered} a=(v^2)/(r) \\ \therefore\Rightarrow \\ v=\sqrt[]{ra} \\ v=\sqrt[]{(5.81*10^7)m\cdot(6.8578\cdot10^6ms^(-2)}) \\ v=7.9520*10^7 \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/physics/college/nsrlwory5nzm3eeilp9m3cs50jsojka6fp.png)
Time period T:

Following is the screenshot of the answer, as per your own request.