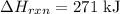Answer
Procedure
To solve this problem you should start by writing down the reaction.
2A+B⇌2C+2D
Now, we will assume that the values represent the respective standard enthalpies of formation for the species that take part in the reaction. Standard enthalpies of formation are measured when one mole of each of these compounds is formed from its constituent elements in their pure state.
In your case, we will have:
A → -275
B →-389
C →185
D →-519
You can calculate the standard enthalpy change of a reaction using the Hess Law that expresses the enthalpy change of reaction by using each individual reaction that corresponds to the standard enthalpy change of formation for the products and for the reactants, as follows:
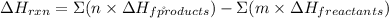
Therefore for our case it will look as
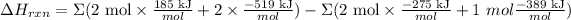
This gives us as result