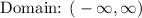A domain of a function is the set of possible numbers that we can input as x. The domain must make the function work and gives you a real y-value.
For example, for a function of f(x) = 1/(x-1), all numbers are possible except for 1 because it will give you a 0 denominator which is not possible. Therefore, the domain for this function is,
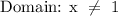
Given the function: f(x) = 2x + 7
All numbers can be its domain, the function will work in all real numbers.
Thus,