We have a binomial process, with n=13 (the number of trials) and p=0.52 (the probability of success).
We have to calculate the probability of these events:
a) Exactly 3 successes.
The probability of k successes in a binomial distribution can be expressed as:
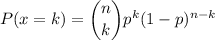
Then, replacing with the known values, we can calculate P(x=3) as:
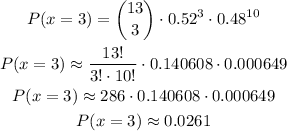
b) At most 11 successes
In this case, we have to calculate P(x<=11) = P(x<12), which means the probability of having less than 12 successes.
This can also be written as:
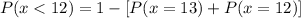
This means that the probability of having less than 12 successes is equal to one less the probability of having 12 or 13 successes.
The probability of 12 successes can be calculated as:
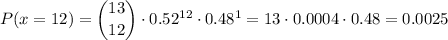
and the probability of 13 successes is:
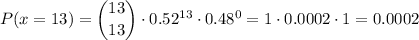
Then, we can replace them in the previous equation and get:
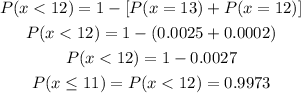
c) At least 2 successes
In this case, we have to calculate P(x>=2).
We then, as we did in the previous point, write this as:
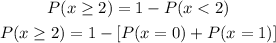
This means that having at least two successes only excludes the probability of having one success, P(x=1), or no success, P(x=0).
We then can calculate P(x=1) and P(x=0) as:
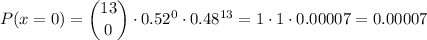
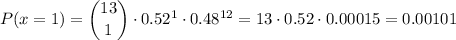
Replacing in the previous equation, we get:
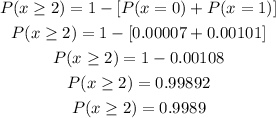
Answer:
a) P(x=3) = 0.0261
b) P(x<=11) = 0.9973
c) P(x>=2) = 0.9989