Given
we are given a function
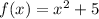
over the interval [0,5].
Required
we need to find formula for Riemann sum and calculate area under the curve over [0,5].
Step-by-step explanation
If we divide interval [a,b] into n equal intervals, then each subinterval has width
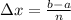
and the endpoints are given by
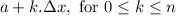
For k=0 and k=n, we get
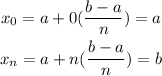
Each rectangle has width and height as
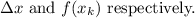
we sum the areas of all rectangles then take the limit n tends to infinity to get area under the curve:
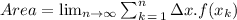
Here
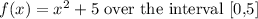
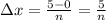
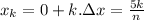
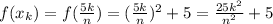
Now Area=
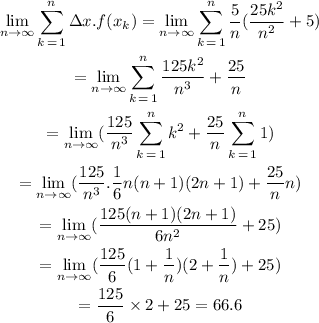
So the required area is 66.6 sq units.