ANSWER:
230.1 pounds
Explanation:
Given:
F1 = 138 pounds
θ1 = 49.2°
F2 = 93 pounds
θ2 = 59.5°
We can better understand the situation by the following sketch:
The vector for 138 pounds at 49.2 is:
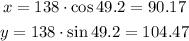
The vector for 93 pounds at 59.5 is
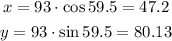
Now, if we add the two vectors to obtain the resulting vector (i.e. the weight):
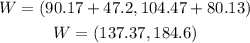
Now, we calculate the normal of this vector W, just like this:

Box weight is 230.1 pounds