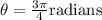Solution:
Given:
![\begin{gathered} \cos (\theta)=-\frac{\sqrt[]{2}}{2} \\ \text{where;} \\ 0\le\theta\le\pi \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/skqkzct2ujgf74kitn98x51ffbgt6w0fnz.png)
![\begin{gathered} \cos (\theta)=-\frac{\sqrt[]{2}}{2} \\ \text{This shows the cosine of the angle has a negative value.} \\ Co\sin e\text{ is negative in the second and third quadrants.} \\ \text{Thus,} \\ \cos (\theta)=-\frac{\sqrt[]{2}}{2} \\ \cos \theta=\frac{\sqrt[]{2}}{2} \\ \cos \theta=(1.4142)/(2) \\ \cos \theta=0.7071 \\ \theta=\cos ^(-1)(0.7071) \\ \theta=45^0 \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/268gxa6k845g9yvopc4u9vw46cbvh4r5ve.png)
In the second quadrant,

We do not need the angle in the third quadrant since the range given is between 0 to 180 degrees and the third quadrant exceeds 180 degrees.
Therefore, the value of the angle in radians in simplified rationalized form is;