Exponential Decay
Some quantities undergo exponential decay which means the rate of decrease is proportional to the current quantity.
A mathematical model for exponential decay is:
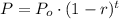
Where:
P: Is the current quantity at time t
Po: Is the initial quantity (at time 0)
r: Is the rate of decay in %
t: Is the time.
The initial quantity of antibiotics is Po = 602 milligrams. The rate of decay is r = 30% = 0.30 per hour. We need to calculate the quantity of antibiotics present after t = 4 hours. Substituting:

Rounding to the nearest tenth:
After 4 hours there will be 144.5 milligrams of antibiotics left