In similar triangles the ratio between corresponding sides is the same in each pair of correspondig sides.
Then, if triangles ABC, ACD and BCD are similars:
Blank 1: Similarity by the Hypotenuse-Leg (HL) criterion
If the ratio between correpondig legs and hypotenuses is equal you can use the pytagorean theorem to prove similarity.
Ratio of corresponding sides in triangles ABC and BCD:
Correspondig sides:
Hypotenuses: c (hypotenuse of triangle ABC) and a (hypotenuse of triangle BCD)
Leg: a (In trinagle ABC) and c-x (in trianlge BCD)
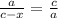
Blank 2: c
Solve a squared:
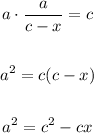
Blank 3: c(c-x)
Ratio of corresponding sides in triangles ABC and ACD:
Correspondig sides:
leg: b (in ABC) and x(in ACD)
Hypotenuse: c (in ABC) and b (in ACD)
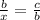
Blank 4: c
Solve b squared:
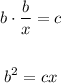
Blank 5: cx
Pythagorean theorem,In a right triangle the sum of legs squared is equal to the hypotenuse squared
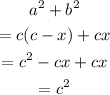
Blank 6: c(c-x)Blank 7: cx
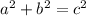
Blank 8: c²