To understand the function better, let's convert it from polar coordinates to cartesian coordinates. The relation between those coordinates are
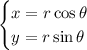
Our function is
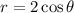
If we multiply both sides by r, we have
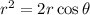
The square of the radius is equal to the sum of the squares of the cartesian coordinates
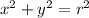
Using this identity, we can rewrite our function as
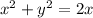
Completing the square, we can rewrite our function as
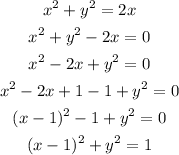
This is a equation of a circle.