If we have a function y=f(x), this means that for an input x we get an output that is y.
If g is the inverse function of f, then x=g(y). This means that when the input is y we get x.
We can write this as:
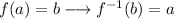
The relation is reciprocal, so if g is the inverse of f, then f is also the inverse of g.
Then, if we have to find f^-1(-1), we have to find the output when the input is -1. That is the same as finding the input of f when the output is -1.
We can look this in the graph as:
We identify the output y=-1 and then we find that f(1)=-1, so the input is x=1. Then, we can write:
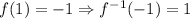
We can repeat the process for f^-1(-3) and f^-1(1):
Then, we have:
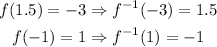
Answer:
1) f^-1(-1) = 1
2) f^-1(-3) = 1.5
3) f^(1) = -1
4) The inverse function inverts the relation between input and output of a function. If the function gives a certain output y for a certain input x, its inverse function will give output x for the input y.