If you compare the functions:
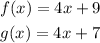
Considering f(x) as the parent function, let's analyze each option:
1) Translation 2 units right.
To translate a function 2 units to the right, you have to subtract 2 to the x-term:
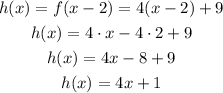
As you can see the resulting function, h(x), is not equal to g(x), which means that the transformation applied was not a shift 2 units to the right.
2) Translation 2 units to the left
To translate the function two units to the left, you have to add 2 to the x-term:
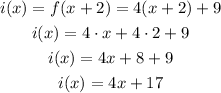
The resulting function, i(x), is not equal to g(x), which means that the transformation applied was not a shift of 2 units to the left.
3) Translation 2 units up
To translate a function 2 units up, you have to add 2 to the function, that is:
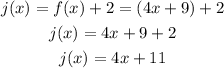
The function j(x) is different from the function g(x), so the transformation applied was not a shift 2 units up.
4) Translation 2 units down
To shift a function two units down, you have to subtract 2 from the function:
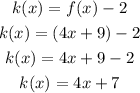
The functions k(x) and g(x) are equal, which means that to determine the function g(x) the function f(x) was translated 2 units down.