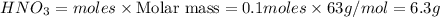Answer: A. 3.28 g of HCl
B. 6.30 g of
Step-by-step explanation:
To calculate the moles :
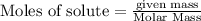
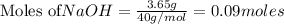
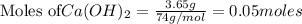
a)
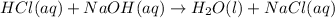
According to stoichiometry :
1 mole of
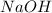 require = 1 mole of
require = 1 mole of
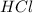
Thus 0.09 moles of
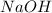 will require=
will require=
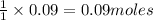 of
of
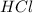
Mass of
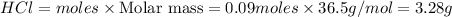
b)
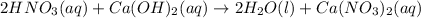
According to stoichiometry :
1 mole of
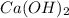 require = 2 moles of
require = 2 moles of
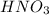
Thus 0.05 moles of
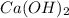 will require=
will require=
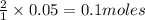 of
of
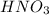
Mass of