In order to calculate the discriminant, let's compare the given equation with the standard form of a quadratic equation, then we use the coefficients in the formula for the discriminant:
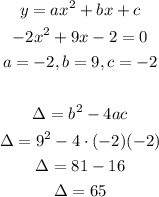
Since the discriminant is greater than 0, that means the quadratic equation has 2 real solutions.