there is no real zero solution and no x-intercept (option C)
Step-by-step explanation:
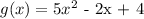
The x intercepts and zeros of a function are the values of x which makes the function equal to zero
We'll make g(x) = 0, then find the values of x
![\begin{gathered} 5x^2\text{ - 2x + 4 = 0} \\ u\sin g\text{ formula method:} \\ x\text{ = }\frac{-b\pm\sqrt[]{b^2-4ac}}{2a} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/w4rfpnctkawm4x6579w7qzpor9iupkdyug.png)
![\begin{gathered} \text{a = 5, b = -2, c = 4} \\ x\text{ = }\frac{-5\pm\sqrt[]{5^2-4(5)(4)}}{2(5)} \\ \\ x\text{ = }\frac{-5\pm\sqrt[]{25-80}}{10} \\ \\ x\text{ = }\frac{-5\pm\sqrt[]{-55}}{10} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/zjoqvcdhn35hyt2t70gplcqevx5v4mkctz.png)
from the above, we have square root of a negative number. We can't solve it without introducing an imagianry number (i). When this is applied, there will be no real roots for x
Hence, there is no real zero solution and no x-intercept (option C)