We need to find the legs of a right triangle.
We know that one of the acute angles is 45º. Since the three internal angles of any triangle must add up to 180º, the other angle A is given by:
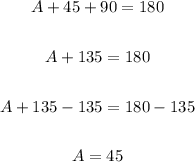
So, both acute angles measure 45º. Since those angles are congruent, so are the legs of the triangle.
Now, calling x the length of each leg, we can use the Pythagorean Theorem to find:
![\begin{gathered} (leg_1)^2+(leg_2)^2=(\text{ hypotenuse})^(2) \\ \\ x^(2)+x^(2)=4^(2) \\ \\ 2x^(2)=4^(2) \\ \\ (2x^2)/(2)=(4^2)/(2) \\ \\ x^(2)=(4^2)/(2) \\ \\ \sqrt[]{x^(2)}=\sqrt[]{(4^2)/(2)} \\ \\ x=\frac{4}{\sqrt[]{2}} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/m8b7x8my42dvq55sr53r80uk3bq71042kz.png)
Therefore, the lengths of the legs are:
![\frac{4}{\sqrt[]{2}}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/or40npqe1l0z1c1ew51hfvodqva20j1kh4.png)