Answer:
a) The workdone to bring the rider and bicycle to a stop = -4900J
b) △x = 21 m
c) Magnitude of the braki
Step-by-step explanation:
The total mass of the rider and the bicycle, m = 60 kg + 7.8 kg
m = 67.8 kg
Speed, v = 12 m/s
The initial kinetic energy of the rider and the bicycle is:
KE = 0.5 mv²
KE = 0.5 x 67.8 x 12²
KE = 4881.6 J
KE = 4900 J (to 2 significant figures)
Since both of them are brought to a stop, the final kinetic energy = 0 J
The workdone to bring the rider and bicycle to a stop = Final Kinetic Energy - Initial Kinetic Energy
The workdone to bring the rider and bicycle to a stop = 0 - 4900
The workdone to bring the rider and bicycle to a stop = -4900J
b) The acceleration is calculated as:
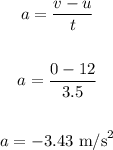
Calculate the distance using the equation of motion

The bicycle travels a distance of 21 m
△x = 21 m
c) The magnitude of the braking force:
