1) How much hydrogen (H2) do we need to produce 180.0 g water (H2O)?
We have to list the known and unknown quantities, check the units and use the ideal gas law.
2) Write the chemical equation
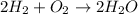
3) List the known and unknown quantities.
P = 0.97 atm.
V = unknown.
n = 180.0 g H2O. n represents the amount of substance. We have to convert this mass to moles.
R = 8.31 L * kPa / mole K.
T = 24 ºC.
4) Set the equation.
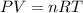
5) Converting units
5.1-Convert kPa to atm.
We can do this change by changing the ideal gas constant.
The new constant is 0.082057 L * atm / mole K
5.2-Convert grams to moles.
The molar mass of water (H2O) is 18.01528 g/mol.
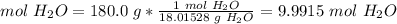
5.3-Convert ºC to K.
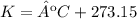
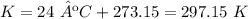
6) Plug in the known quantities in the ideal gas equation and solve for V.
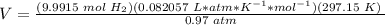
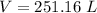
Errors found.
1) The chemistry teacher used the molar ratio between H2 and H2O from an unbalanced chemical equation.
2) The chemistry teacher plugged in grams instead of moles in the ideal gas equation.
3) The chemistry teacher plugged in degrees Celsius instead of Kelvin in the ideal gas equation.
4) There was a conflict regarding pressure units. The ideal gas constant had pressure in kilopascal (kPa) and the measurement was taken using atmospheres (atm).