Given the information on the problem, we have that the population is normally distributed, then, the test statistic is the following:
![Z=\frac{\bar{X}-\mu}{\frac{\sigma}{\sqrt[]{n}}}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/high-school/h5idfem2zuffllcnvn9svhd4q5gv3lzy9r.png)
in this case we have:
![\begin{gathered} \bar{X}=58 \\ \mu=81.2 \\ \sigma=17.9 \\ n=11 \\ \Rightarrow Z=\frac{58-81.2}{\frac{17.9}{\sqrt[]{11}}}=(-23.2)/(5.397)=-4.298 \\ Z=-4.298 \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/high-school/l4a71ok01m1y4anh8qw0ftwxhqaur93org.png)
then, the test statistic is Z = -4.298.
For the p-value, notice that since we want to test the hypothesis H1: mu < 81.2, the p-value of the test is the probability that a random sample of size 11 will have a mean of 58 or les if the real mean would be 81.2, this is:
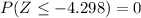
therefore, the p-value is 0