The given system of equations is,
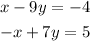
A system of equations can be defined as,
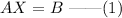
Here, A is the ceofficient matrix, X is the variable matrix and B is the constant matrix.
Coefficient matrix gives the coefficients of the variables in the system of equations. Hence,
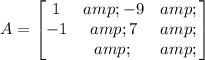
Hence, equation (1) can be written as,
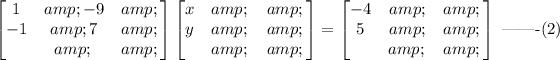
If a 2x2 matrix A is given by,
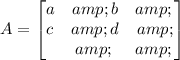
Then, adj A is, Hence, the adjoint of the given matrix A is,
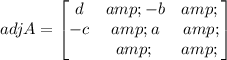
The determinat of A is,
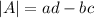
Hence, the inverse of the given matrix A is,
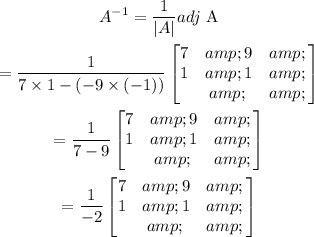
Now, multiply equation (1) by inverse of A to solve for the variable matrix.
![\begin{gathered} A^(-1)AX=A^(-1)B \\ IX=A^(-1)B \\ \begin{bmatrix}{1} & {0} & {} \\ {0} & {1} & {} \\ {} & {} & {}\end{bmatrix}\begin{bmatrix}{x} & {} & {} \\ {y} & {} & {} \\ {} & {} & {}\end{bmatrix}=(1)/(-2)\begin{bmatrix}{7} & {9} & {} \\ {1} & {1} & {} \\ {} & {} & {}\end{bmatrix}\begin{bmatrix}{-4} & & {} \\ {5} & & {} \\ {} & {} & {}\end{bmatrix} \\ \begin{bmatrix}{x} & {} & {} \\ {y} & {} & {} \\ {} & {} & {}\end{bmatrix}=\begin{bmatrix}{(-7)/(2)} & {(-9)/(2)} & {} \\ {(-1)/(2)} & {(-1)/(2)} & {} \\ {} & {} & {}\end{bmatrix}\begin{bmatrix}{-4} & & {} \\ {5} & & {} \\ {} & {} & {}\end{bmatrix} \\ \begin{bmatrix}{x} & {} & {} \\ {y} & {} & {} \\ {} & {} & {}\end{bmatrix}=\begin{bmatrix}{(-7)/(2)*(-4)+((-9)/(2)*5)} & & {} \\ {(-1)/(2)*(-4)+((-1)/(2)*5} & {} & {} \\ {} & {} & {}\end{bmatrix} \\ \begin{bmatrix}{x} & & {} \\ {y} & & {} \\ {} & {} & {}\end{bmatrix}=\begin{bmatrix}{14-(45)/(2)} & & {} \\ {2-(5)/(2)} & & {} \\ {} & {} & {}\end{bmatrix} \\ \begin{bmatrix}{x} & {} & {} \\ {y} & {} & {} \\ {} & {} & {}\end{bmatrix}=\begin{bmatrix}{(-17)/(2)} & & {} \\ {(-1)/(2)} & & {} \\ {} & {} & {}\end{bmatrix} \end{gathered}]()
Here, I is identity matrix.
Therefore, the inverse of matrix A is,
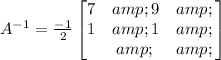
x=-17/2 and y=-1/2.